
The polarities and current directions are reversed here compared to NPN transistor. Here the base terminal has negative bias with respect to emitter and the emitter terminal has positive bias voltage with respect to both base and collector because of PNP transistor. The circuit connection of PNP transistor with supply voltages is given below. The emitter voltage is much positive with respect to base and collector.

Here if you observe, the base current flows out of the base unlike NPN transistor. This transistor mainly consists of 3 terminals and they are Emitter (E), Collector (C) and Base (B). The above figure shows the structure and symbol of PNP Transistor. The symbol and structure for PNP transistor is shown below. But the characteristics and operation of the PNP transistor is almost same as NPN transistor with small differences. The structure of PNP transistor is completely opposite to the NPN transistor. In PNP transistor this arrow indicates as ‘pointing in’ and the current direction in PNP is completely opposite to the NPN transistor. The arrow for BJT transistors is always located on the emitter terminal and also it indicates the direction of conventional current flow. The small base current in the PNP has the ability to control the large emitter-collector current because it is a current-controlled device. In PNP, the current sinks in to the base terminal. All the supply voltage polarities applied to the PNP transistor are reversed. In PNP transistor, the majority current carriers are holes and electrons are the minority current carriers. The two PN-junction diodes in the PNP transistor structure are reversed with respect to the NPN transistor, such as the two P-type doped semiconductor materials are separated by a thin layer of N-type doped semiconductor material. The structure of the PNP transistor is completely different from the NPN transistor. I have searched on google but I can't 100% understand it.PNP transistor is another type of Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT).
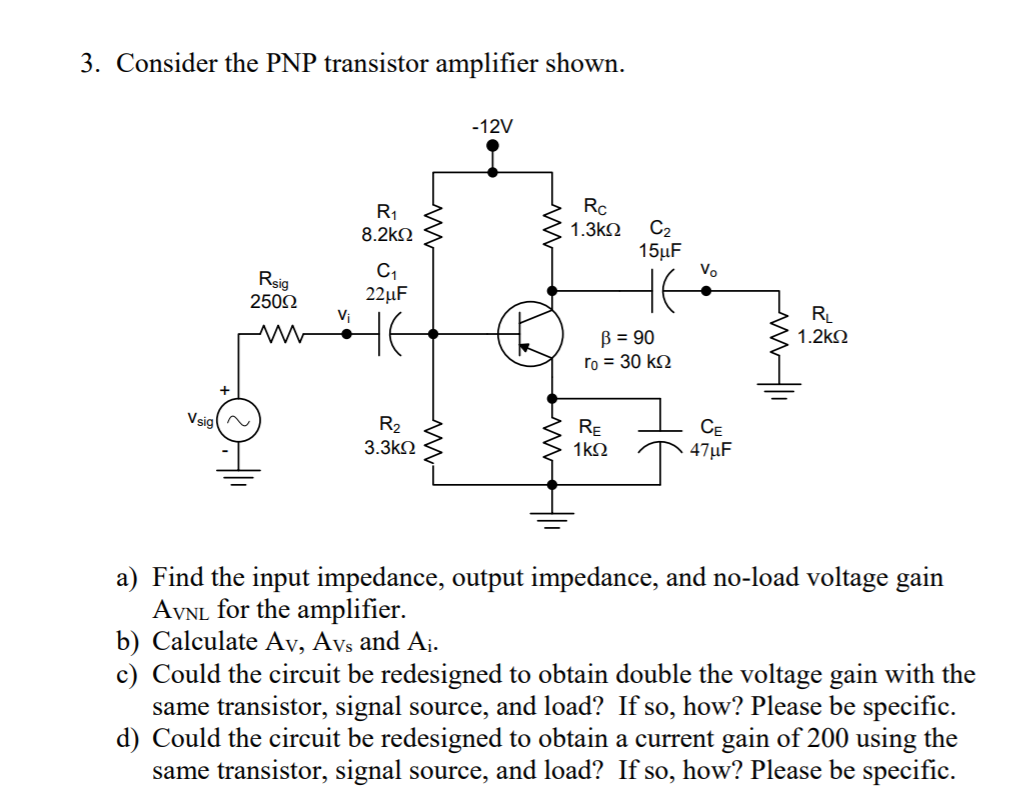
How this entire thing works based on voltage amplification based on my circuit.
#3 resistor npn transistor amplifier how to#
I also understood the voltage gain based on Rc and RE for example if Rc = 1k and Re = 100 ohm the gain is 10.īut I cant understand how to choose a resistor and how much current should I use how much current to amplify to amplify the voltage, and how much voltage to give to get 10V as output. I understood that the amount of voltage we give in input to the base we will get as large voltage between collector and emitter based on the resistors.

Its maximum output voltage is 3.3V but I need 10V so I planned to use an NPN transistor in common emitter configuration so that I can amplify 3.3V to 10V and then I can give that to the gate of the MOSFET. I am using STM32 micro controller for controlling. I want to give 10V input to the gate of the MOSFET to get very low Rds. In my circuit I need to amplify 3.3V of my stm32 micro controller input to 10 V output to drive a Mosfet switch. I have basic knowledge about NPN transistors and I know how they work: for current gain based on the small input current in the base we are able to drive large amount of current in between collector and emitter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
